Calculate your Body Mass Index
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on your height and weight that is applicable to men and women. You can either consult the BMI chart or use the BMI calculator provided below to determine your body mass index.
Body Mass Index calculator
Enter your weight, height, age, and gender using standard or metric units in the BMI calculator below:
Adult Body Mass Index table
What is a good BMI? The guideline is between 18.5 and 24.9 for a healthy BMI. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have established the following categories for adults based on their Body Mass Index (BMI):
| BMI | Weight Status |
|---|---|
| Less than 16 | Severely underweight |
| 16 to 17 | Moderately underweight |
| 17 to 18.5 | Mildly underweight |
| 17 to 18.5 | Healthy weight |
| 25 to 30 | Overweight |
| 30 to 35 | Obese class I |
| 35 to 40 | Obese class II |
| Greater than 40 | Obese class III |
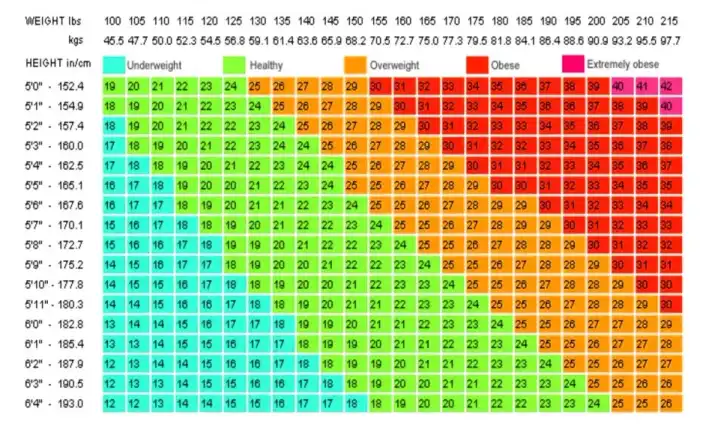
BMI chart
Find below a general adult BMI chart.
Understand the BMI measurement
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a way to measure a person's body composition based on their height and weight. It is commonly used as a general indicator of whether someone has a healthy weight for their height. The BMI calculator result value is used to classify a person as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese based on certain ranges. These BMI ranges may vary depending on factors such as age and gender. While BMI is not a perfect measure of healthy weight, it can be a useful tool to determine if additional testing or action is necessary. See the table for the different categories based on BMI used by the body mass index calculator.
The potential negative health effects of having a high BMI
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), being overweight or obese can increase the risk for a number of health conditions, including:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease such as heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Certain types of cancer such as endometrial, breast, colon and kidney cancer
- Sleep apnea and respiratory problems
- Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Infertility
- Increased risk of falling and breaking bones
- Higher risk of death from any cause.
The potential negative health effects of having a low BMI
- Malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies
- Anemia
- Osteoporosis, a disease that causes bone weakness, increasing the risk of breaking a bone
- A decrease in immune function
- Growth and development issues, particularly in children and teenagers
- Possible reproductive issues for women due to hormonal imbalances that can disrupt the menstrual cycle. Underweight women also have a higher chance of miscarriage in the first trimester
- Potential complications as a result of surgery
- Generally, an increased risk of mortality compared to those with a healthy BMI.
How to calculate BMI?
BMI is determined by using the formula: BMI = 703 x weight (in pounds) / height (in inches)^2. Individuals with a weight less than 50 pounds or greater than or equal to 650 pounds, a height less than 3 feet or greater than or equal to 8 feet, a BMI less than 12 or greater than or equal to 100. Pregnant individuals were excluded from the study. Our BMI calculator uses this formula.
BMI formula: 703 x weight [lbs]⁄height [in]2
Problems of the Body Mass Index (BMI) calculation.
The Body Mass Index (BMI) calculation has several limitations, such as:
- It does not take into account differences in muscle mass, bone density, and distribution of fat, which can lead to inaccuracies in determining a person's overall health status. For example, athletes and bodybuilders may have a high BMI due to their muscle mass, but may not be considered overweight or unhealthy.
- It does not distinguish between fat mass and lean mass, which can lead to misclassification of individuals as overweight or obese when they may not be.
- It does not consider the location of the body fat. For example, people who have a lot of abdominal fat are at a higher risk for health problems than those who have fat primarily in other areas of the body.
- It does not take into account the health risks for certain populations, such as older adults or certain ethnic groups.
- It does not take into account the overall health status and medical history of an individual.
- It may not be a good indicator of health for older adults, as muscle mass decreases with age and that may lead to a higher BMI but with less muscle mass.
- It is not suitable for pregnant or lactating women, athletes, or people who are very muscular.
Therefore, it's important to consider other factors such as body composition, waist circumference, and overall health status before making conclusions about health risks based on BMI. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for a more accurate assessment of your health status.